Over the past few years, Portuguese legislation has been subject to significant changes that have directly impacted the taxation of share deals which value results, directly or indirectly, from Portuguese real estate assets.
Portuguese corporate income tax reform
The Law No. 2/2014 of January 16 approved the reform of the Portuguese corporate income tax (CIT), which had the main purpose of promoting the competitiveness and internationalisation of Portuguese companies through the implementation of several measures. Among these measures, the introduction of the participation exemption regime can be highlighted.
Participation exemption regime
Portugal has reviewed the participation exemption regime which applies to Portuguese resident companies holding a qualifying participation. The participation exemption is applicable not only to dividends but also to capital gains from the sale of shares, provided certain requirements are complied with – resulting in a full CIT exemption.
However, there is an exception to this rule, which refers to capital gains realised upon the sale of real estate companies (i.e. companies whose assets are comprised of, in more than 50%, real estate located in Portugal). As a result, the participation exemption regime is not applicable to capital gains derived from the sale of such companies, even if the seller is a Portuguese corporate shareholder.
However, the participation exemption may still apply if the real estate assets are used by the real estate company for carrying out an agricultural, industrial or commercial activity, other than the purchase and resale of immovable property (e.g. short-term rental, hotels, factories, office buildings, etc.).
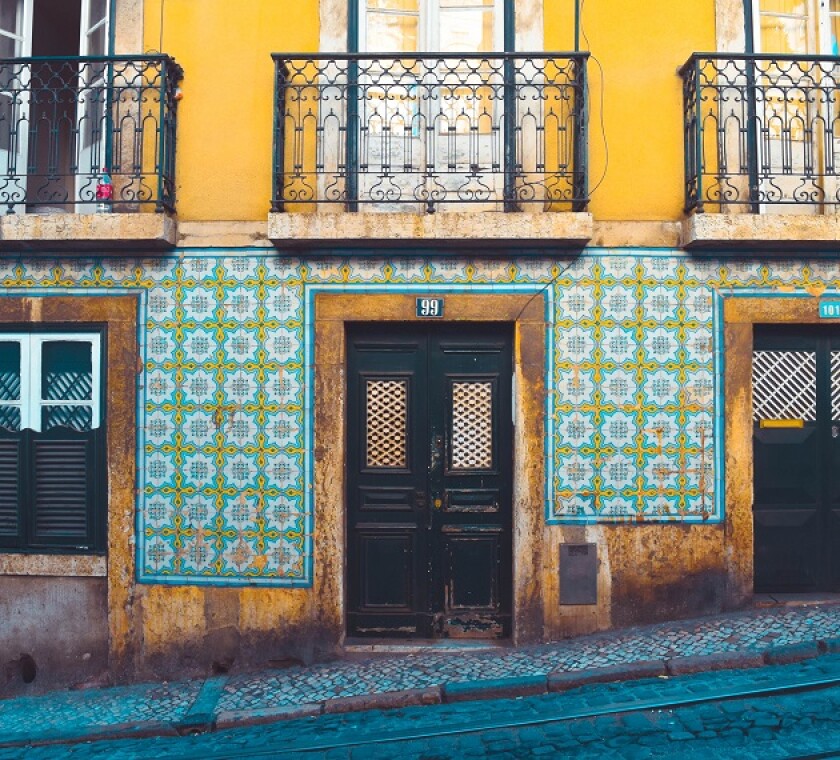
In Scenario 1 depicted below, which represents a domestic situation, under the Portuguese participation regime, capital gains may benefit from a full exemption even if it is a real estate company (provided that it is used for carrying out an agricultural, industrial or commercial activity).
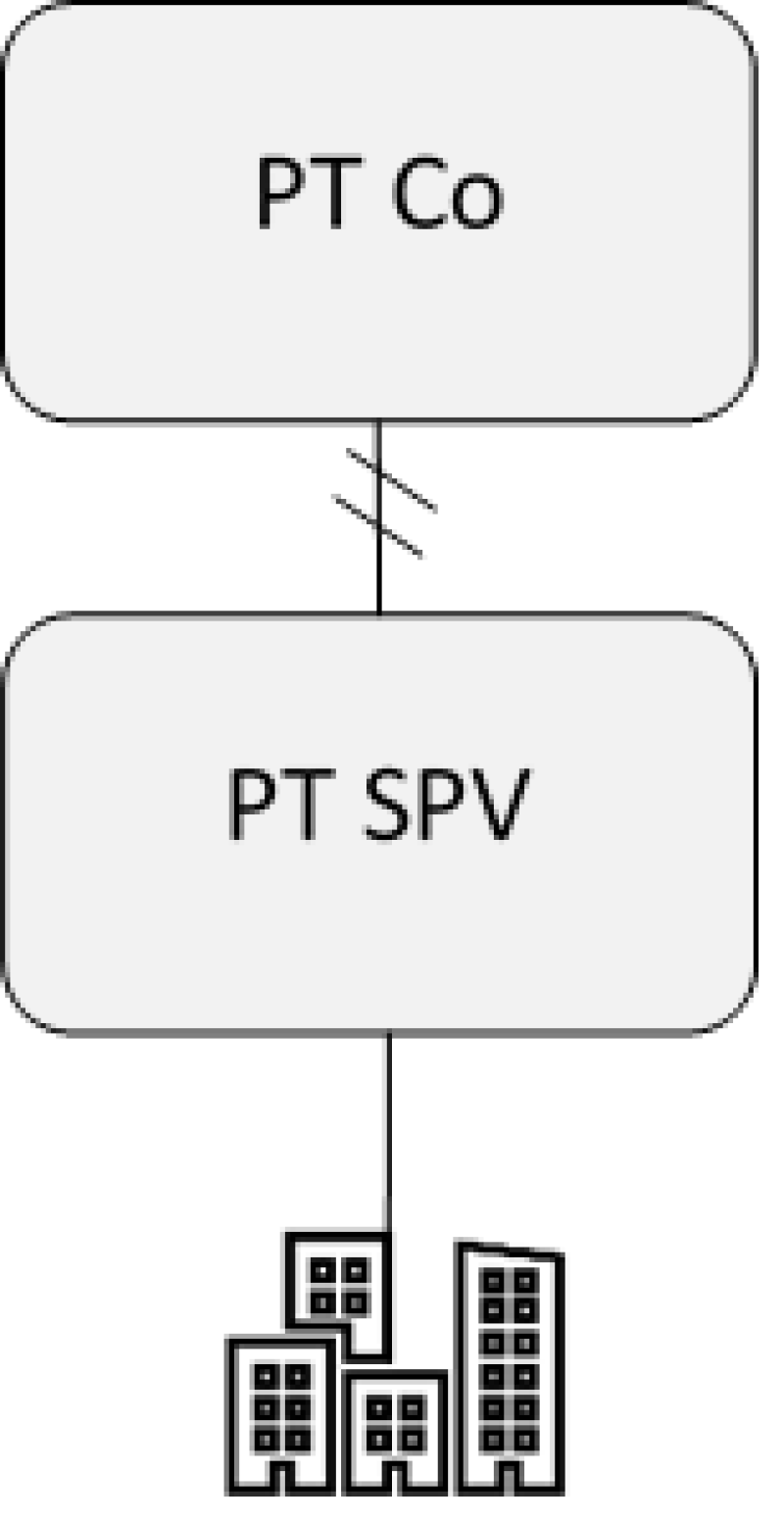
Scenario 1
Portuguese state budget law for 2018
The State Budget Law for 2018 introduced a new provision in the CIT code, according to which capital gains derived from the sale of a foreign entity are also taxable in Portugal provided that, at any point in time during the 365 days prior the sale of the shares, the latter derived more than 50% of their value directly or indirectly from immovable property located in Portugal.
Before this rule, Portuguese taxation would only be triggered if (at least) the real estate company was a resident entity. The new provision extended the Portuguese jurisdiction to tax transactions that have no direct connecting link with a Portuguese territory.
In Scenario 2 below, the authors have depicted a transaction where capital gains realised from the sale of shares in a foreign company (i.e. where all transaction is carried out outside Portugal) became taxable in Portugal as from January 1 2018.
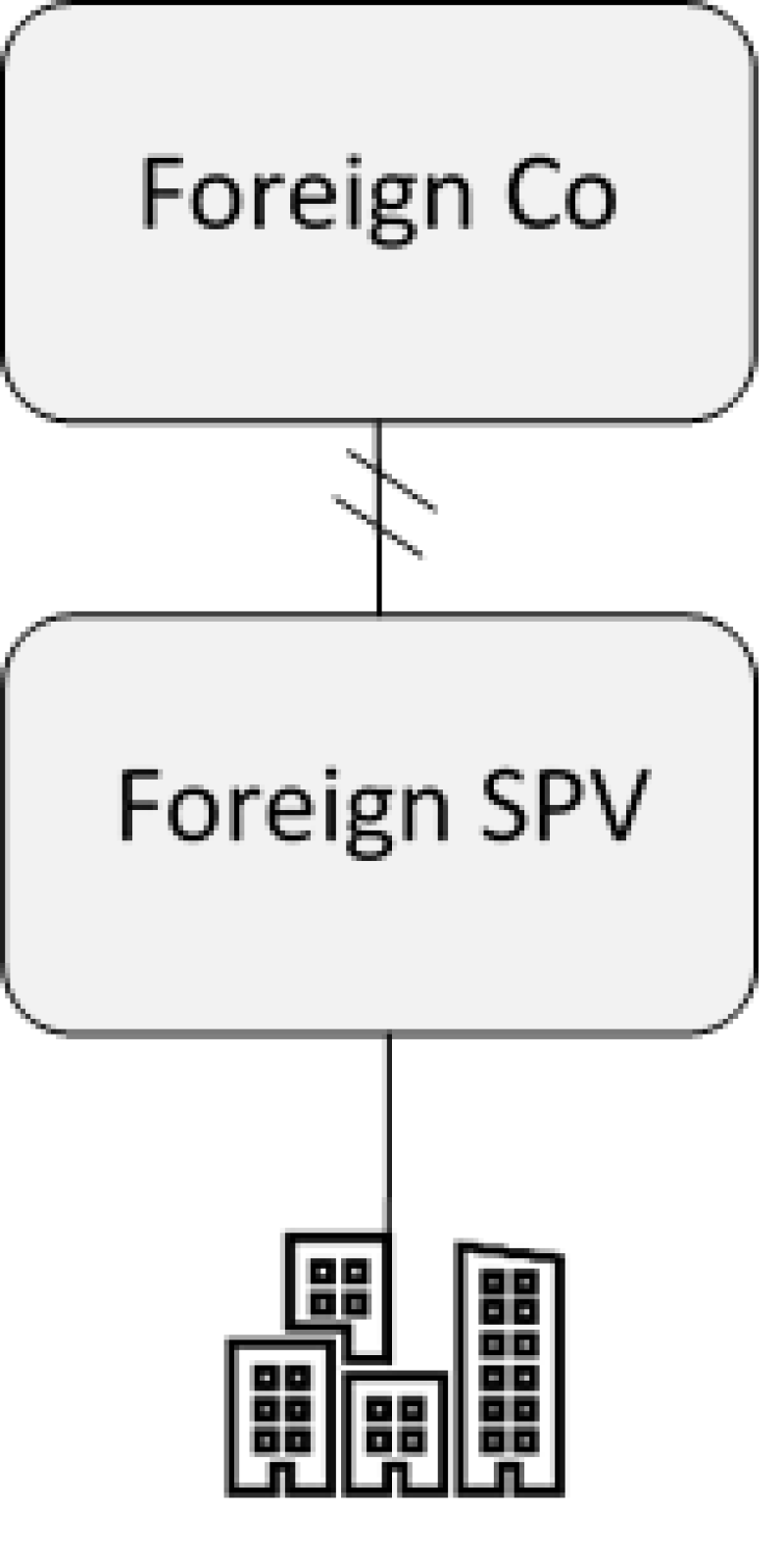
Scenario 2
Portuguese state budget law for 2019
The State Budget for 2019 has introduced amendments to the Tax Benefits Code, complementing the above 2018 amendment to the CIT code and providing for capital gains’ exemption similar to the one applicable to purely domestic transactions.
From 2018 onwards, capital gains from the transfer of shares in non-resident entities became potentially taxable, whenever, at any point in time during the 365 days prior to said transfer, the value of the shares resulted directly or indirectly in more than 50% of immovable property located in Portugal. The 2019 amendment to the Tax Benefits Code allowed said capital gains to still qualify for a full CIT exemption provided that the assets are used for carrying out an agricultural, industrial or commercial activity, other than the purchase and resale of real estate.
Unfortunately, it seems that the Portuguese legislator overlooked a very common situation, where the shareholder (seller) is a foreign company and the target is a Portuguese real estate company.
Contrary to Scenario 1 and Scenario 2, in the case of the transfer of shares of a Portuguese entity by a foreign shareholder – we should look at Scenario 3 – where capital gains arising from such sales remain subject to taxation without the possibility to claim the exemption based on the effective use of the immovable property. Therefore, even if the Portuguese real estate company carries out a business and uses its real estate assets – agricultural, industrial or commercial activities, there will be no possibility (under current tax provisions) to claim a tax exemption upon sale. This situation clearly affects international groups investing in Portugal in standard “real estate based businesses”, such as hotels, other accommodation services, call centres, co-working spaces, agribusiness, etc.
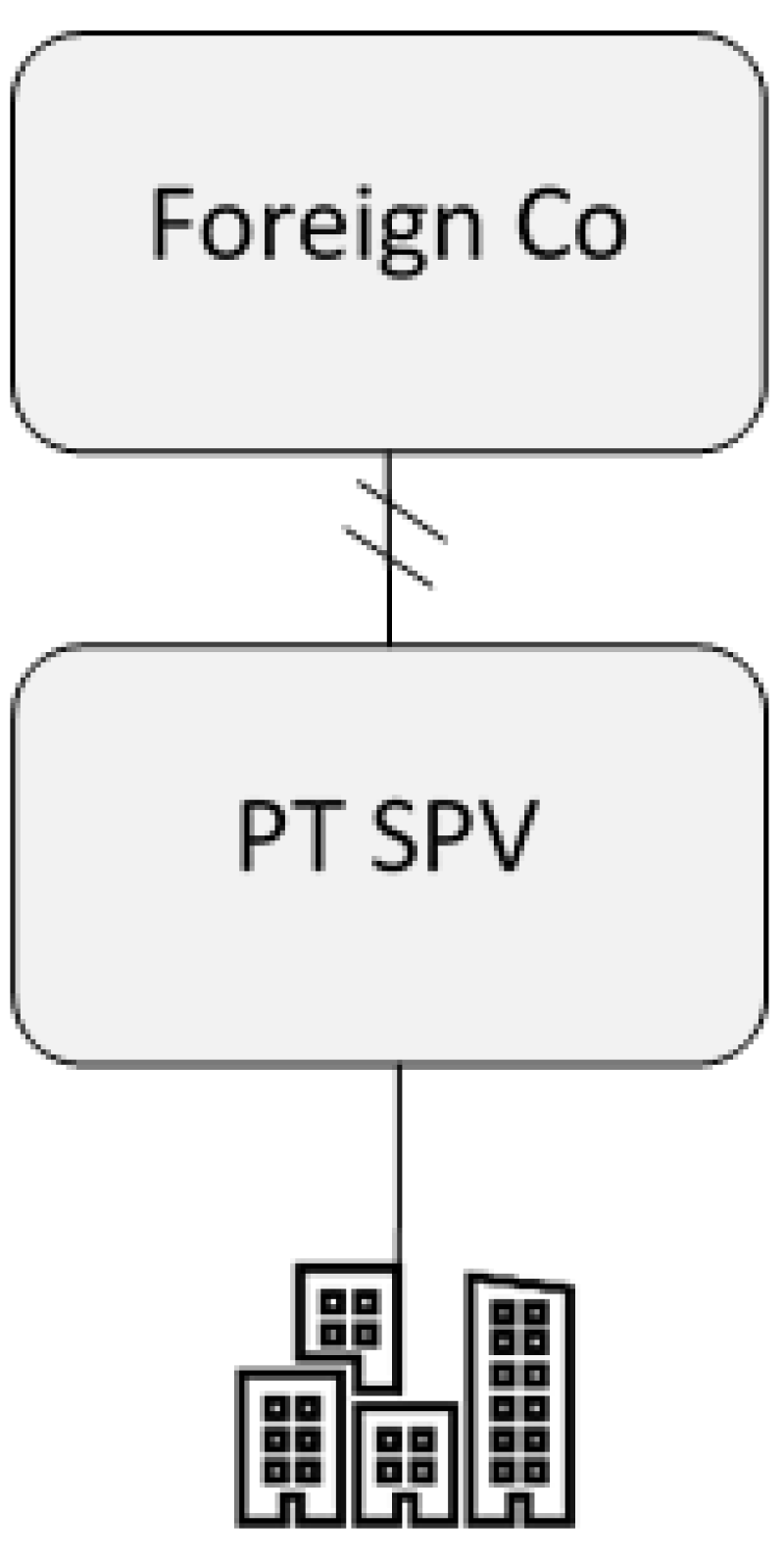
Scenario 3
The different tax treatment between Scenarios 1, 2 and 3 clearly constitutes a discrimination that hinders the freedom of establishment and the free movement of capital, as foreseen in the Treaty of Functioning of the European Union (TFEU). Therefore, while this discriminatory treatment remains in force, it is likely that the said breach of EU law gives rise to tax litigation and possibly to a referral to the European Court of Justice for a preliminary ruling.
Francisco Cabral Matos
T: +351 213 113 485
E: fcm@vda.pt
Mélanie Pereira
T: +351 213 113 400
E: mpp@vda.pt













