As countries begin the economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, 69% of the 131 tax professionals who responded to ITR's survey expect governments to increase environmental taxes on multinational enterprises (MNEs) to pay for the deficit.
At the same time, attention is turning once more to climate change, precipitated by the end, in some countries, of a crisis-level pandemic. US President Biden’s return to the Paris Agreement on climate has reinforced this trend, and 61% of respondents think that the change of US administration will cause environmental taxes on MNEs to increase.
In the future, tax professionals foresee changes in the way that environmental taxes are levied. These taxes traditionally fall under indirect tax, but 42% of respondents to ITR’s survey said that governments could introduce corporate income taxes based on environmental impact.
As the momentum for environmental taxes builds, MNEs are facing pressure from all directions to take responsibility for their environmental impact. A full commentary on the survey results will be published online and in ITR’s summer magazine in June.
Have national governments and international organisations (OECD/EU/UN) shown an increased interest in environmental tax policy over the past year?
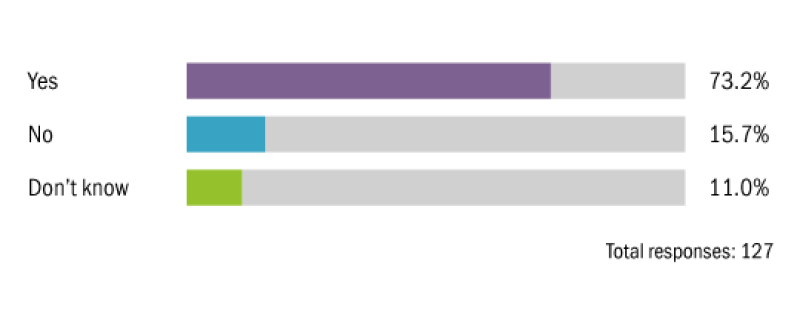
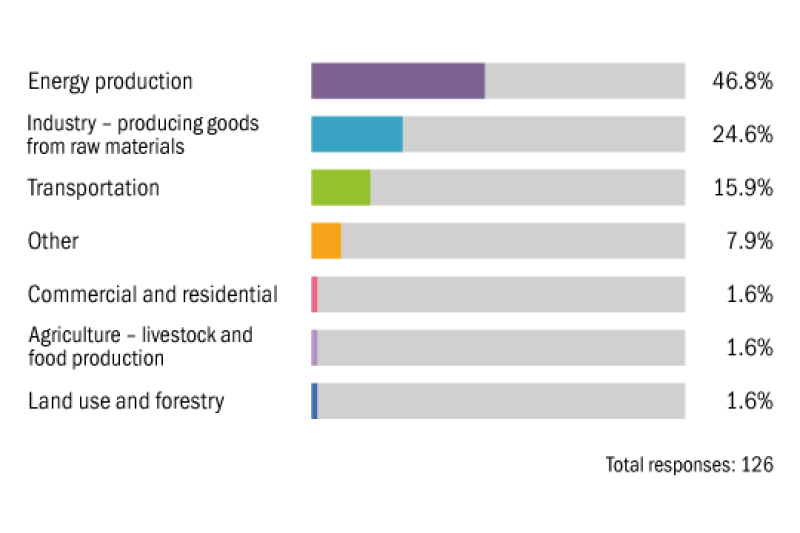
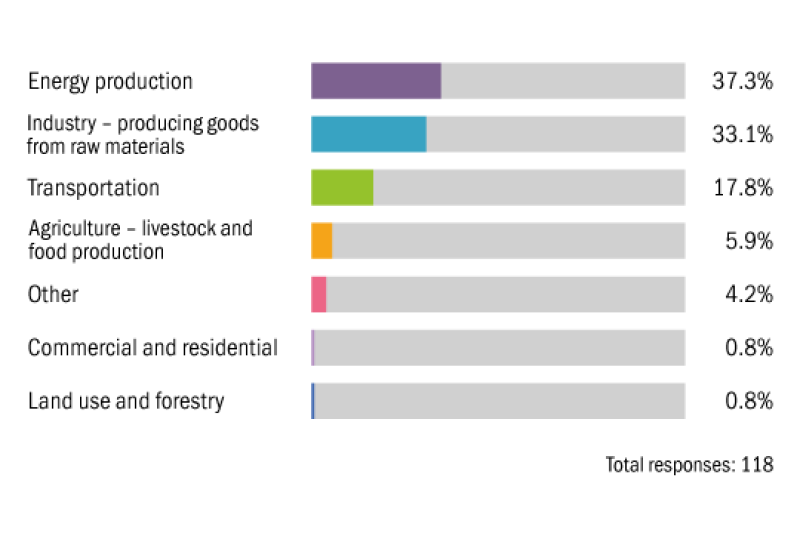
Which sector is currently targeted the most by environmental tax policies?
Do you think the change of US administration from Trump to Biden will (directly or indirectly) increase environmental taxes on multinationals?
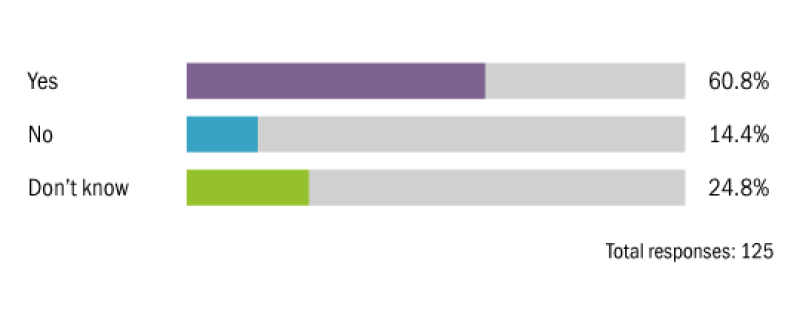
From which direction are companies facing the most pressure to increase environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) measures?
Which of the following measures would companies prefer to tackle carbon emissions?
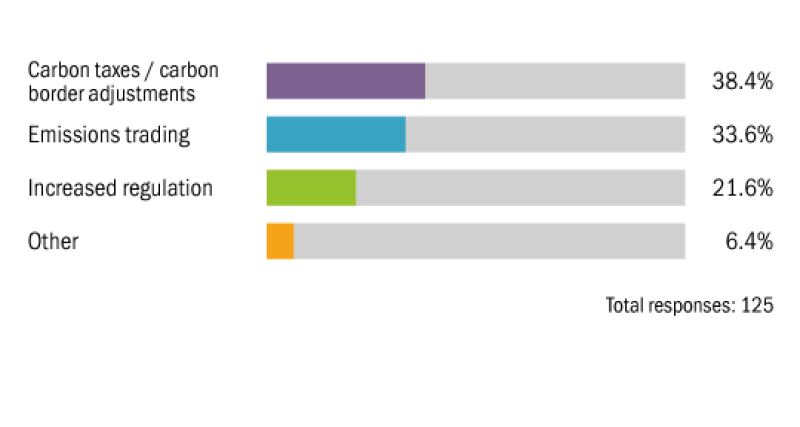
Governments are providing sufficient tax incentives for companies to reduce pollution and develop the green economy.
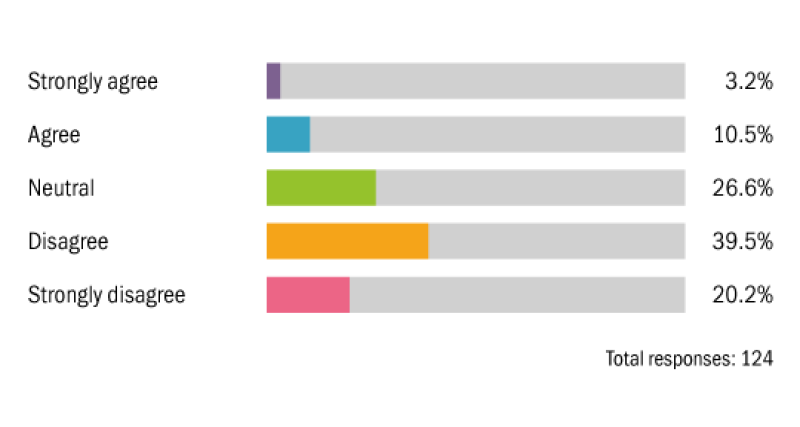
Governments and international bodies will rely primarily on taxation (as opposed to other measures, like regulation) to tackle environmental damage.
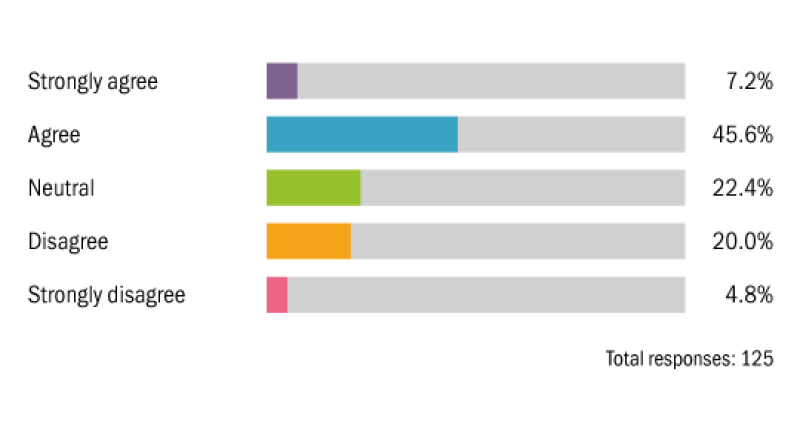
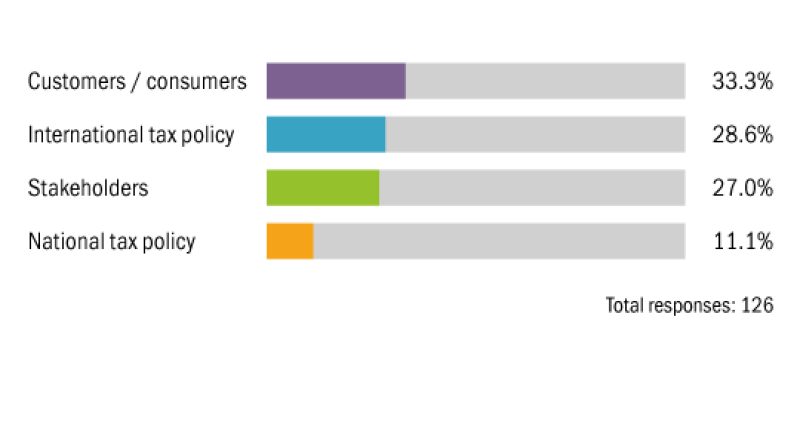
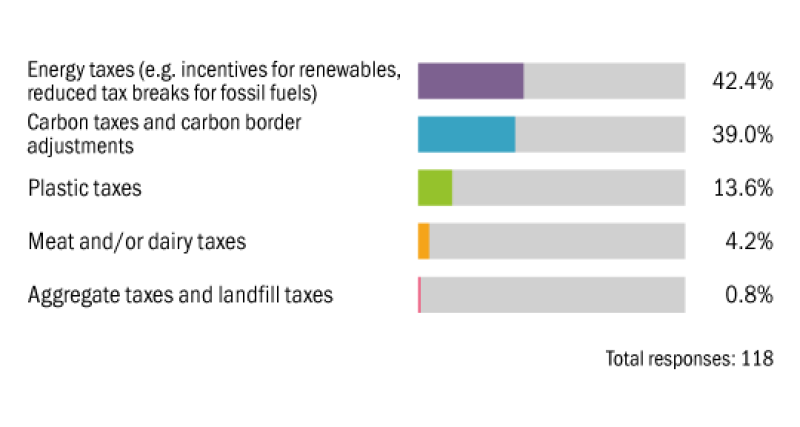
Which area of tax will be the main focus of future environmental taxation?
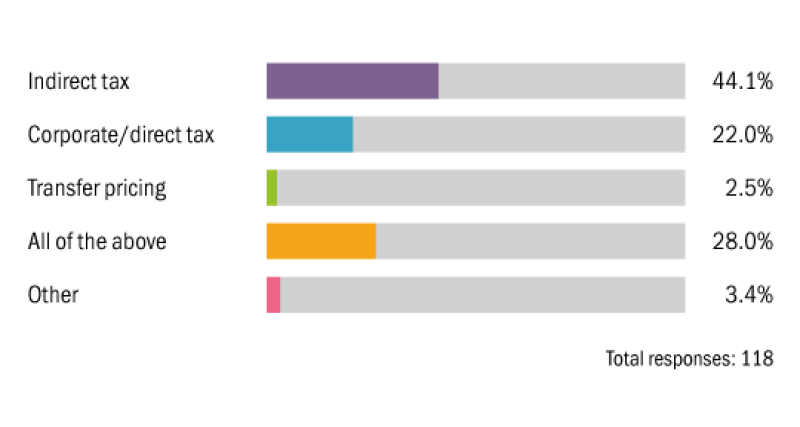
Do you expect governments to introduce corporate income taxes based on environmental impact to encourage more environmentally friendly activities in the future?
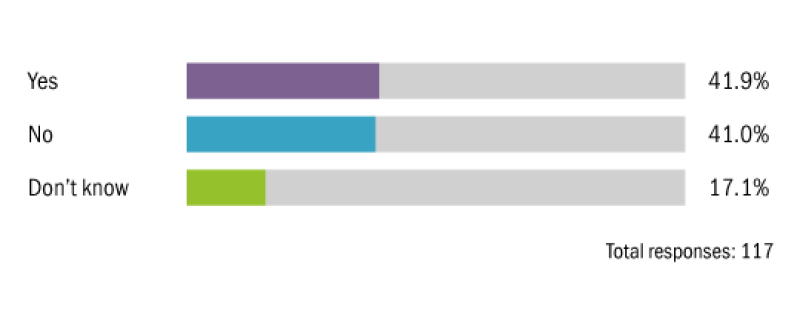
Which sector will be targeted the most by future environmental tax policies?
In-house tax teams will play a significant role in deciding future environmental tax policy.
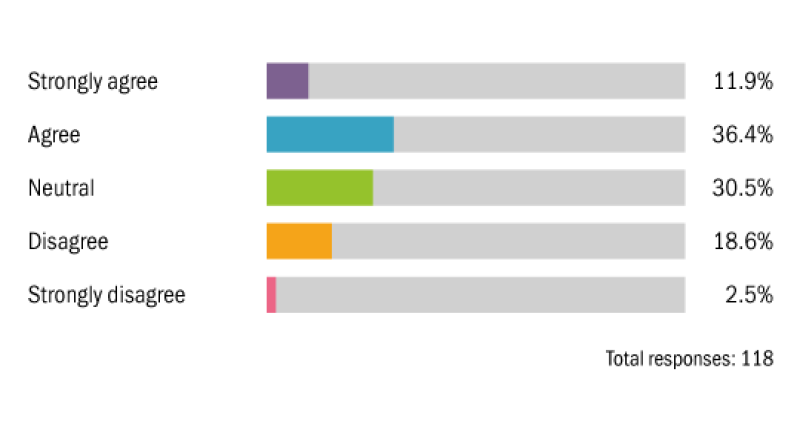
Do you expect the post-COVID-19 economic pressure on governments to lead to more environmental taxes?
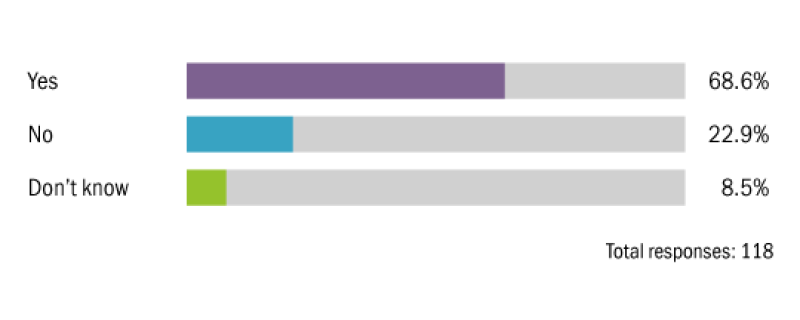
To what extent should in-house tax teams at multinational companies be planning for environmental tax changes?
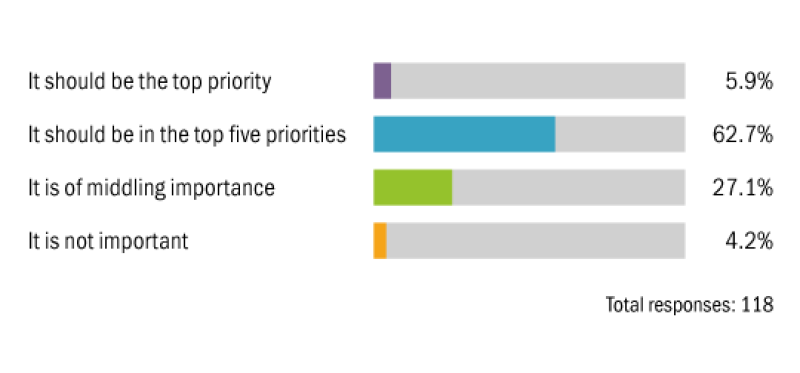
Where do you expect to see the most change in environmental taxes in the coming years?
Carbon border taxes will have a significant impact on global commerce and supply chains in the next five years.
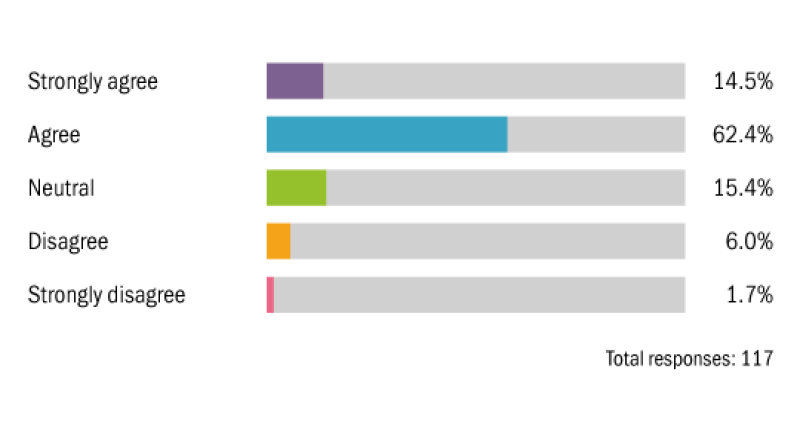
Will governments begin to commit to phasing out tax breaks for fossil fuels in the coming years?
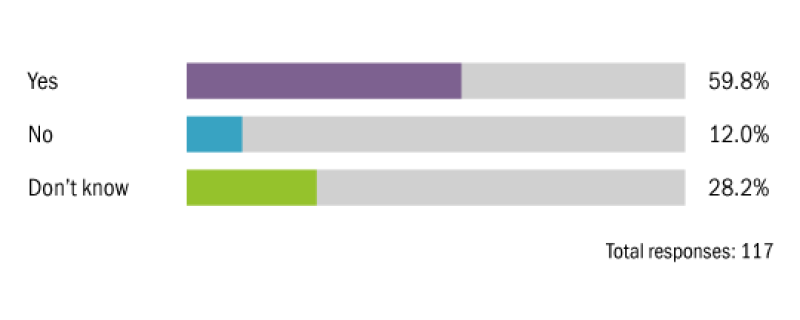
What industry is your company in?
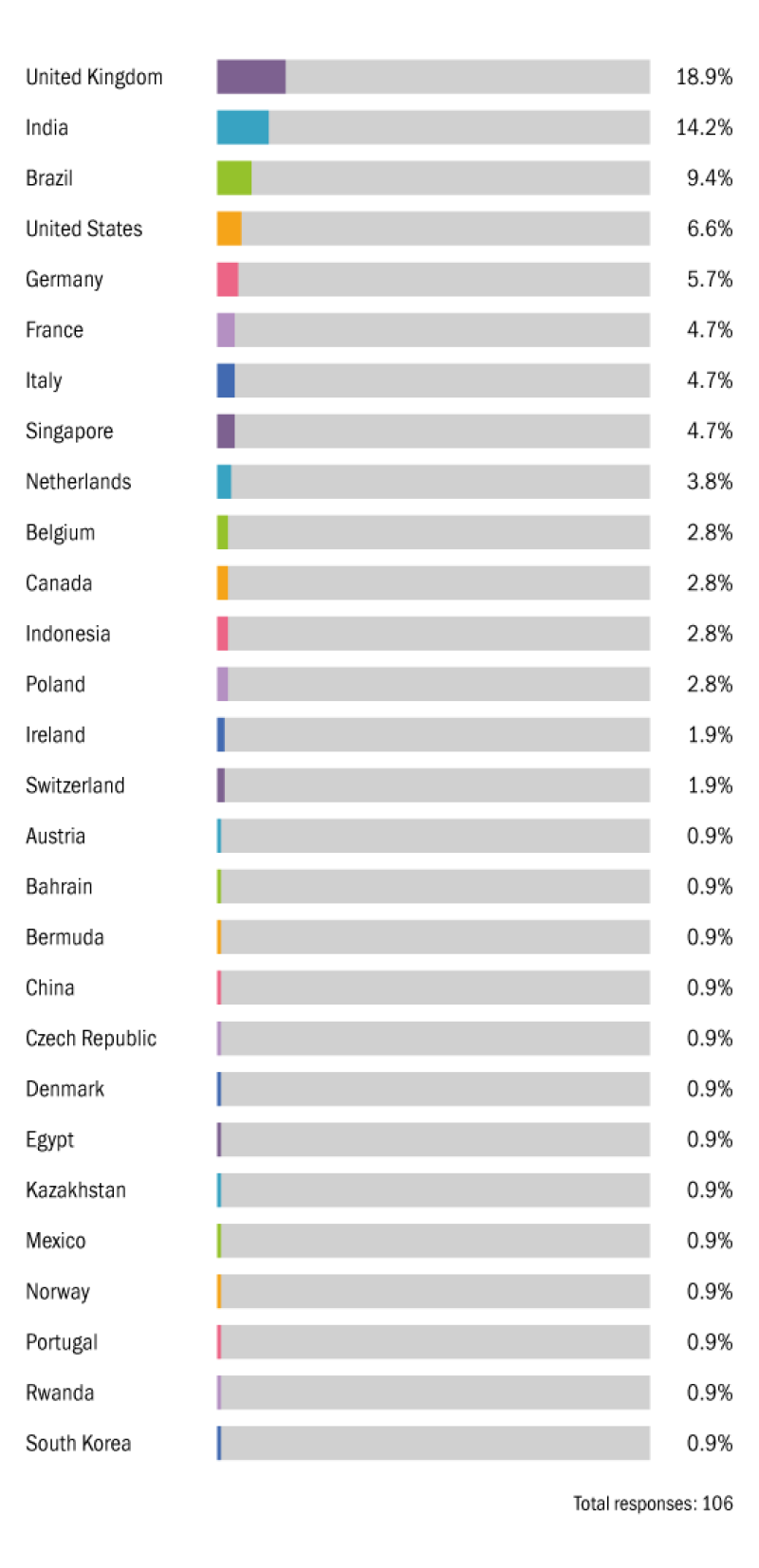
What country do you work in?